



Some Helpful Tools
Math: Area - Tutorial
Finding the Area of Quadrilaterals
Area is the number of square units that will fit inside of a figure. Finding the area is like finding the amount of tile it will take to cover a kitchen floor.
A square is a quadrilateral figure with four equal sides and four right angles.
The formula for the area of a square is:
This section will cover the fundamentals and rules for finding the area.
Example 1: Find the area of the square.
The formula for the area of a rectangle is:
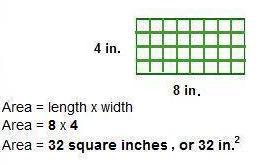
Area = length x width
Example 2: Find the area of the rectangle.

A parallelogram is a quadrilateral (plane figure with four sides) where the opposite sides are parallel and have equal sides.
The formula for the area of a parallelogram is:
Area = base x height
Example 3: Find the area of the parallelogram.
A trapezoid is a quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides, which are called bases.
The formula for the area of a trapezoid is:
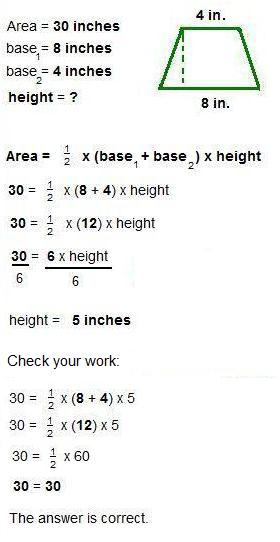
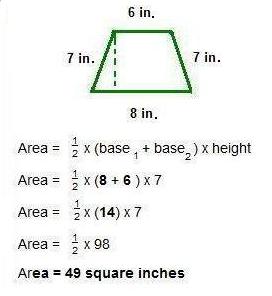
Example 4: Find the area of the trapezoid.
A triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles.
The formula of the area of a triangle is:
A circle is a shape that will points the same distance from its center.
The formula for the area of a circle is:
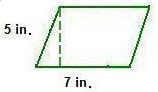
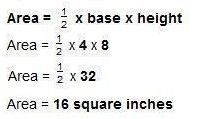
Area = base x height
Area = 7 x 5
Area = 35 square inches
Example 5: Find the height of the trapezoid.
Finding the Area of a Circle

Example: Find the area of the circle:

Finding the Area of Polygons
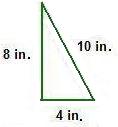
Example 1: Find the area of the triangle.
Hint: Multiply the base and height. Then
divide by 2.
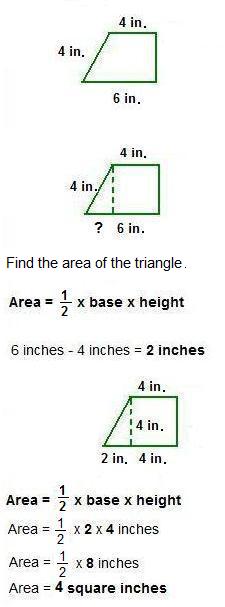
Example 2: Find the height of the triangle.

Example 3: Find the area of the polygon.

A rectangle is a quadrilateral figure with two long equal sides and two short equal sides and four right angles.
Hint: Multiplying times a fraction means to divide by the denominator of that fraction.
In this case, divide by 2.
Geometry is a type of math that focuses on the study of shapes and measurements and relations to points, lines, angles, surfaces, and solids.