Some Helpful Tools
This section will cover the fundamentals of verbs and how they are used.
How to Identify a Verb
Rules for Verbs
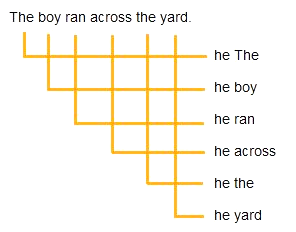
The boy ran across the yard.
What did the boy do? boy ran
An apple fell from the tree.
What did the apple do? apple fell
Susan baked a pie.
What did Susan do? Susan baked
The workers arrived early.
What did the workers do? workers arrived
The result that makes the most sense is: he ran. Therefore, ran is the verb.
Verbs show whether something has happened in the past, the present, or the future. This is called verb tense.
There are twelve tenses altogether. For more on verb tenses, see our Verb Tenses section.
Some verbs are regular verbs, which means that only the ending of the verb is changed within some of the tenses. However, the base remains the same.
Verbs use tense to describe when the action of a sentence is taking place. These verbs may require a helping verb.
Verbs must agree with their subjects.
Regular verbs are conjugated differently from irregular verbs.
For a list of irregular verbs, click here.
Linking verbs do not show action. They link the subject to its description.
Conjugating Verbs
The following verbs are conjugated in the present tense.
Susan will be visiting her grandparents on Saturday. (future tense)
Dave and Maria are planning a vacation for next spring. (present tense)
I could have slept for a few more hours. (past tense)
More on Verbs
Verbs that end in ing are used with helping verbs is, am, and are. These verbs are called the present participle. They are used to form the continuous tenses:
He is singing
I am playing
They are learning
Verbs that are used with the past tense of have form the past participle.
had sung had played had learned
Verb Tenses
Helping verbs are attached to the main verb to help describe when the action
will occur.
Helping verbs are also known as auxiliary verbs.
Below are a few examples of helping verbs:
Helping Verbs
Remember to add the following helping verbs: has or have to the past participle
to create the present perfect tense.
The conjugated form of to be is a linking verb as well as a helping verb.
Reminder 1: Linking verbs appear in front of an adjective, noun, or pronoun to form a subject complement.
Janet is a dentist. (noun)
Darren is excited about the trip. (adjective)
It was he who called about the ad. (pronoun)
Reminder 2: Helping verbs appear in front of another verb.
George is arriving on Friday.
Noli will be visiting her sister in Utah.
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs link subjects to adjectives, nouns, and pronouns to create subject complements.
is
am
are
be
was
were
been
being
appear
seem
become
That child is sleepy.
Harold seems excited about the new job.
Option 1: Look for the word that shows what action the subject is doing.
Option 2: Put the pronoun he in front of each word in the sentence below.
A linking verb is the main verb in the sentence.
Below are some common linking verbs:
am
are
is
was
were
be
being
been
have
has
had
do
does
did
could
should
would
can
shall
will
may
might
must
Linking Verbs and Helping Verbs
For more helping verbs, click here.
For more linking verbs, click here.
1.
2.
3.
4.
I am
you are
he, she, it is
we are
you (pl) are
they are
I do
you do
he, she, it does
we do
you (pl) do
they do
I have
you have
he, she, it has
we have
you (pl) have
they have
The following verbs are conjugated in the simple past tense.
I was
you were
he, she, it was
we were
you (pl) were
they were
I did
you did
he, she, it did
we did
you (pl) did
they did
I had
you had
he, she, it had
we had
you (pl) had
they had
The following verbs are conjugated in the past participle tense.
I have had
you have had
he, she, it has had
we have had
you (pl) have had
they have had
I have done
you have done
he, she, it has done
we have done
you (pl) have done
they have done
I have been
you have been
he, she, it has been
we have been
you (pl) have been
they have been
Mira has done her chores for the day.
They have finished the assignment already.
Add had to the past participle to create the past perfect tense.
Mira had done her chores by the time her mother came home.
They had finished the assignment just before the bell rang.
Verb tenses are covered in more detail in the Verb Tenses section.
Language Arts: Verbs - Tutorial