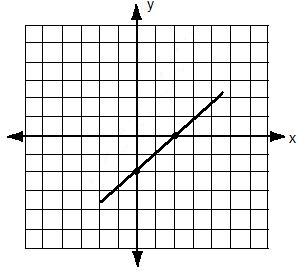
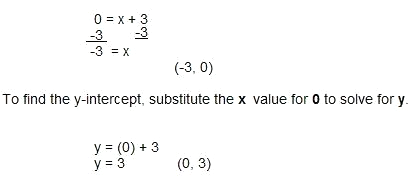Example 3: y = x + 3
To find the x-intercept, substitute the y value for 0 to solve for x.
Some Helpful Tools
The x-intercept intercepts the x-axis.
The y-intercept intercepts the y-axis.
An intercept involves an equation, which requires finding two different solutions for the coordinates of the x-intercept and the y-intercept.
Once you have found your solutions, you will be able to do the following:
- plot your points
- draw a line to connect the points
When finding a solution to an equation, no matter where you are on the x-axis, the value for y will always be 0.
Also, no matter where you are on the y-axis, the value for x will always be 0.
The reason is because the axis lines intersect at (0,0). So the x-axis is always 0 while the y-axis is also always 0. These values will always stay constant.
This section will cover the fundamentals and rules of an intercept.
The X-Intercept and the Y-Intercept
Finding Coordinates
Example 1: y = x - 2
To find the x-intercept, substitute the y value for 0 to solve for x.
0 = x - 2
+2 +2
2 = x (2, 0)
Next, find the y-intercept. Substitute the x value for 0 to solve for y.
y = x - 2
y = 0 - 2
y = -2 (0, -2)
Now that you have both of your x and y coordinates, plot them in the coordinate plane.
Linear equations will usually have many solutions of ordered pairs to plot in a coordinate plane. Intercepts have two solutions (one for the x-intercept and one for the y-intercept).
The x-intercept is (2,0). The y-intercept is (0,-6).
The x-intercept is (-3,0). The y-intercept is (0,3).
When you look at an intercept, you are looking at a line that crosses or intersects another line.
Math: Intercepts - Tutorial