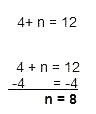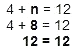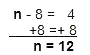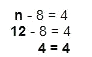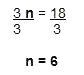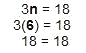Some Helpful Tools
Subtraction
This section will cover the fundamentals of solving one-step equations using variables.
Variables in an Equation
The examples above are called expressions. An expression becomes an equation when it contains an equal sign.
Equations are two expresions that equal each other. The next step is to solve for the variable n.
In the mutliplication example shown above , 3n, is written as: 3 times n.
The 3 is called a coefficient.
When no number appears in front of the variable, we assume the coefficient is 1.
Addition
When adding, we do the inverse of or "undo" the operation to solve for the variable.
Example:
You can check to see if the answer is correct, by plugging the answer back into the equation. If both sides are equal, the answer is correct.
The answer is correct.
Hint: The inverse of addition is subtraction. Since
we're adding 4, we'll subtract 4 from both sides to solve for n.
When subtracting, we do the inverse of or "undo" the operation to solve for the variable.
Example:
Hint: The inverse of subtraction is addition. Since we're subtracting 8, we'll add 8 to both sides to solve for n.
Check your work:
The answer is correct.
Multiplication
When multiplying, we do the inverse of or "undo" the operation to solve for the variable.
Example:
n - 8 = 4
3n = 18
Hint: The inverse of multiplication is division. Since we're multiplying n times 3, we'll divide 3 by both sides to solve for n.
Check your work:
The answer is correct.
Division
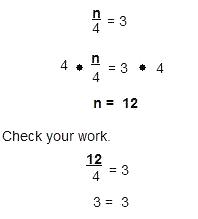
When dividing, we do the inverse of or "undo" the operation to solve for the variable.
Example:
The answer is correct.
Hint: The inverse of division is multiplication. Since we're dividing n by 4, we'll multiply both sides by 4 to solve for n.
One-Step Equations using variables are just the beginning for solving algebraic problems.
A variable in an equation is only useful when you know what number the variable represents.
Math: One-Step Equations - Tutorial